
What is Constipation?
Constipation is a digestive condition characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stools, and/or hard, dry stools. It can cause discomfort and pain, and can also lead to complications, such as fecal impaction or rectal bleeding.

What are the symptoms of constipation?
The symptoms of constipation can vary from person to person, but some common symptoms include:
- Infrequent bowel movements: Having fewer than three bowel movements per week is considered constipation.
- Hard, dry stools: Stools that are difficult to pass, small in size, and dry and hard are common symptoms of constipation.
- Straining during bowel movements: Constipation can cause discomfort and require extra effort to pass stools.
- Abdominal pain: Constipation can cause cramping, bloating, and pain in the abdomen.
- Nausea: Some people with constipation may experience nausea or vomiting.
- Rectal bleeding: Infrequent bowel movements and straining can cause small tears in the anus and rectum, leading to rectal bleeding.
- Incomplete evacuation: The feeling of not completely emptying the bowels after a bowel movement is a common symptom of constipation.
If you are experiencing symptoms of constipation, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.

Who’s affected?
Constipation can affect anyone, but certain groups of people are at higher risk, including:
Women: Women are more likely to experience constipation than men, particularly during pregnancy and menopause.
Older adults: Constipation becomes more common as people age due to changes in diet, physical activity, and metabolism.
People with sedentary lifestyles: A lack of physical activity can slow down digestion and increase the risk of constipation.
People with certain medical conditions: Chronic conditions such as IBS, IBD, hypothyroidism, and Parkinson’s disease can increase the risk of constipation.
People who take certain medications: Certain medications, such as opioids, antacids containing calcium or aluminum, and anticonvulsants, can cause constipation.
It’s important to keep in mind that everyone’s digestion is unique and that factors such as diet, lifestyle, and overall health can also affect the likelihood of developing constipation. If you’re experiencing symptoms of constipation, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How common is constipation?
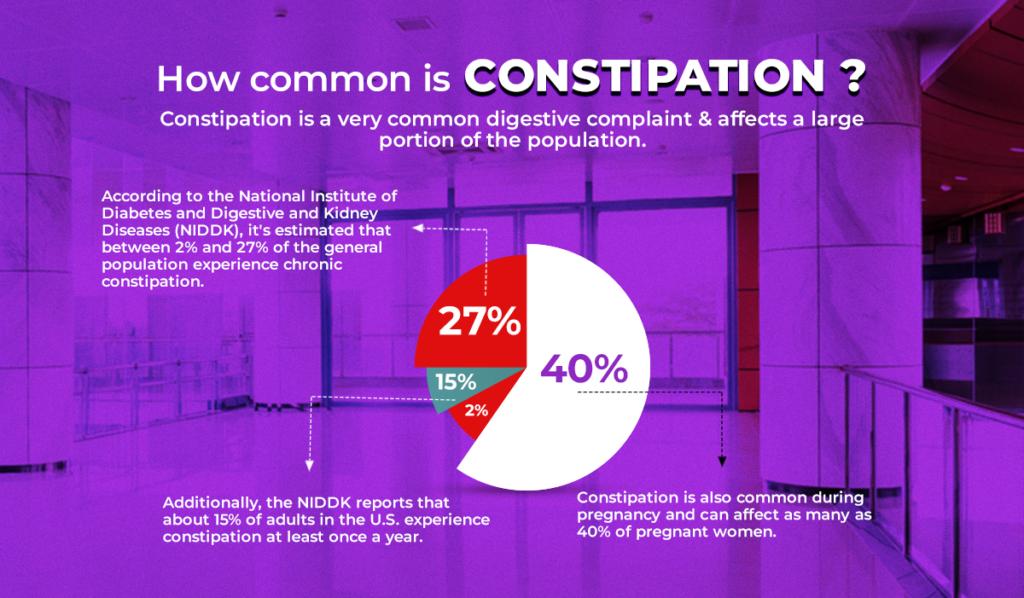
Constipation is a very common digestive complaint and affects a large portion of the population. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), it’s estimated that between 2% and 27% of the general population experience chronic constipation. Additionally, the NIDDK reports that about 15% of adults in the U.S. experience constipation at least once a year. Constipation is also common during pregnancy and can affect as many as 40% of pregnant women. Overall, the prevalence of constipation suggests that it’s a common digestive issue that affects a significant portion of the population.
How does constipation happen?
Constipation occurs when stool moves too slowly through the digestive system, causing it to become hard and difficult to pass. This can be caused by several factors, including:
- Diet: Low-fiber diets, dehydration, and a lack of fluids can contribute to constipation.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can slow down digestion and lead to constipation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as opioids, antacids containing calcium or aluminum, and anticonvulsants, can cause constipation.
- Medical conditions: Constipation can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as IBS, IBD, hypothyroidism, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Aging: As people age, muscle tone in the intestines may decrease, leading to constipation.
- Changes in routine: Travel, changes in diet or physical activity, and stress can disrupt normal bowel patterns and lead to constipation.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the rectum and intestines from the growing uterus can cause constipation during pregnancy.
8. Poor sleep habits: Insufficient sleep or sleep disturbances can affect digestion and contribute to constipation.
9. Stress: Stress can disrupt the digestive process and lead to constipation.
10. Ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement: Holding in stools for too long can cause them to become harder and more difficult to pass.
It’s important to keep in mind that everyone’s digestion is unique and that factors such as diet, lifestyle, and overall health can also affect the likelihood of developing constipation. If you’re experiencing symptoms of constipation, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.

How is constipation treated?
Constipation can often be relieved using simple home remedies, including:
Fiber: Increase fiber intake by eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. This can help to soften the stool and make it easier to pass.
Fluids: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to help soften the stool and prevent dehydration.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help stimulate the muscles in the digestive system and promote regular bowel movements. Try yoga poses; certain yoga poses, such as pelvic tilts and cat-cow stretches, can help stimulate the muscles in the intestines and promote bowel movements.
Probiotics: Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet, such as yogurt and kefir, may help regulate digestion and prevent constipation.
Over-the-counter remedies: Some over-the-counter remedies, such as fiber supplements, stool softeners, and lubricants, can help relieve symptoms of constipation.
Coffee: Drinking a cup of coffee in the morning can help stimulate the muscles in the digestive system and promote bowel movements.
Warm bath: Soaking in a warm bath can help relax the muscles in the digestive system and stimulate bowel movement.
Herbs and spices: Some herbs and spices, such as ginger, fennel, and peppermint, have been used for their digestive benefits and can help relieve symptoms of constipation.
Magnesium: Magnesium supplements may help relax the muscles in the digestive system and promote regular bowel movements.
Castor oil: Castor oil is a natural lubricant that may help soften the stool and relieve constipation.
Natural Prunes: Some natural remedies for constipation include prunes, prune juice, which can help add bulk to stools and improve bowel movements.

Constipation during pregnancy
Constipation during pregnancy is a common problem and can occur due to a number of factors, including hormonal changes, increased pressure on the rectum and intestines from the growing uterus, and a lack of physical activity. Symptoms of constipation during pregnancy include infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stools, and hard, dry stools. If left untreated, constipation can lead to discomfort and rectal bleeding, and it can also increase the risk of pregnancy complications, such as gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia.
How can I prevent constipation?
Here are some ways to prevent constipation:
Eat a high-fiber diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet to help promote regular bowel movements.
Drink enough fluids: Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day to help prevent dehydration and soften the stool.
Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help stimulate the muscles in the digestive system and promote regular bowel movements.
Maintain a regular routine: Try to have regular bowel movements at the same time each day and avoid ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement.
Avoid foods that can cause constipation: Processed foods, dairy products, foods high in fat and sugar, red meat and fried foods can slow down digestion and lead to constipation.
Manage stress: Stress can disrupt the digestive process and lead to constipation. Try to practice stress-management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
Get enough sleep: Aim to get 7-8 hours of sleep each night to help regulate digestion and prevent constipation.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of constipation, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Chronic constipation treatment
Treatment for chronic constipation may include a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Some effective treatments for chronic constipation include:
Diet changes: Increasing fiber and fluid intake, and avoiding foods that can worsen symptoms, such as dairy products, processed foods, and caffeine.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help stimulate bowel movements and improve gut health.
Bowel training: Establishing regular bathroom habits, such as going at the same time each day, can help regulate bowel movements.
Medications: Over-the-counter stool softeners, fiber supplements, lubricants, and osmotic laxatives can help relieve constipation.
Probiotics: Probiotics can help improve gut health and promote regular bowel movements.
Biofeedback therapy: Biofeedback therapy can teach patients to identify and control the muscles involved in defecation, leading to improved bowel movements.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to correct underlying medical conditions that are contributing to chronic constipation.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to determine the best course of treatment for chronic constipation. Treatment may vary based on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4059-constipation
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/constipation
https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/digestive-diseases-constipation





