
Are you looking for urinary tract infection health information? Because you’ve arrived at the right place. If you want to know how urinary tract infection (UTI) affects your health, this is the article for you.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
Every year, approximately 150 million people worldwide suffer from urinary tract infections, according to studies. A UTI is an infection that occurs in the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, and ureters. It is caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra and spreading to the bladder. However, it is treatable through antibiotics and other natural remedies.
Prevalence of UTIs
UTI is a common infection, and it can affect anyone at any age. Approximately 60-70% of UTIs (Urinary Tract Infections) occur in women, while 30-40% occur in men. Women are more prone to UTIs due to their anatomy because they have a shorter urethra. Children can also develop UTIs although it is less common.

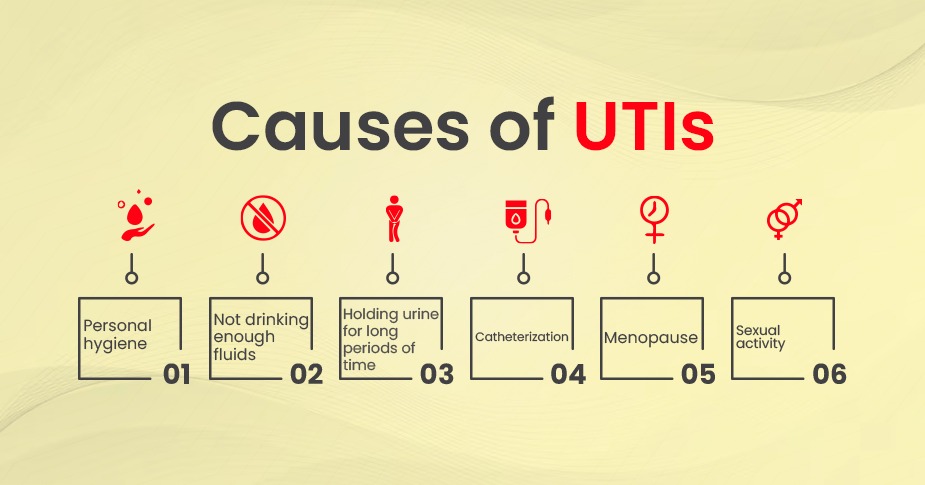
Causes of UTIs
- Personal hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, such as not wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Not drinking enough fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Holding urine for long periods of time: Urinating on a regular basis can help prevent bacteria from building up in the urinary tract.
- Catheterization: The use of a catheter to drain the bladder can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Menopause: Losing estrogen after menopause can cause changes in the urinary tract that make UTIs more likely.
- Sexual activity: UTIs are more common in women who are sexually active, and they may be more likely to occur after sexual intercourse.
- Use of a diaphragm or spermicide: These methods of birth control can increase the risk of UTIs
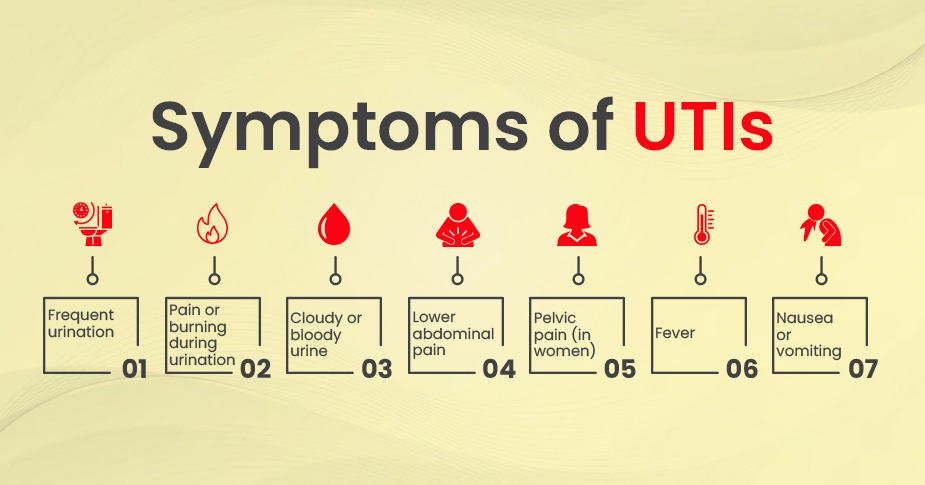
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of UTI can vary depending on the location of the infection and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Frequent urination: You may need to urinate more frequently than usual, even if you do not produce much urine.
- Pain or burning during urination: You may experience discomfort or a burning sensation when you urinate.
- Cloudy or bloody urine: UTIs can cause the urine to appear cloudy or to contain blood.
- Lower abdominal pain: You may experience pain or discomfort in your lower abdomen.
- Pelvic pain (in women): UTIs can cause pain in the pelvic area in women.
- Fever: If the UTI spreads to the kidneys, you may develop a fever.
- Nausea or vomiting: These symptoms may occur if the UTI spreads to the kidneys.
Diagnosis of UTIs
UTIs are usually diagnosed using a combination of a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common test used to diagnose a UTI is a urinalysis, which involves analyzing a sample of your urine to look for signs of infection, such as white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria. A urine culture may also be done to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and to determine the most appropriate antibiotic for treatment.
Treatment of UTIs
You should seek medical attention if you believe you have a UTI
Here are some home remedies and medical treatments that may help alleviate UTIs
- Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, helps ease pain and discomfort.
- Using a heating pad or taking a warm bath to help alleviate cramping and pain.
- Applying a cold pack to the lower abdomen to help reduce inflammation.
- Drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry supplements may help prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder and urinary tract walls.
- Using products with ursolia helps reduce inflammation associated with UTIs.
- Consuming vitamin C which helps to boost the immune system and may help to fight off infection.
- Involves antibiotics, which can be taken orally or intravenously.
- A specific antibiotic used will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the severity of the infection.
It is important to finish the entire course of treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider to ensure that the disease is fully eliminated.
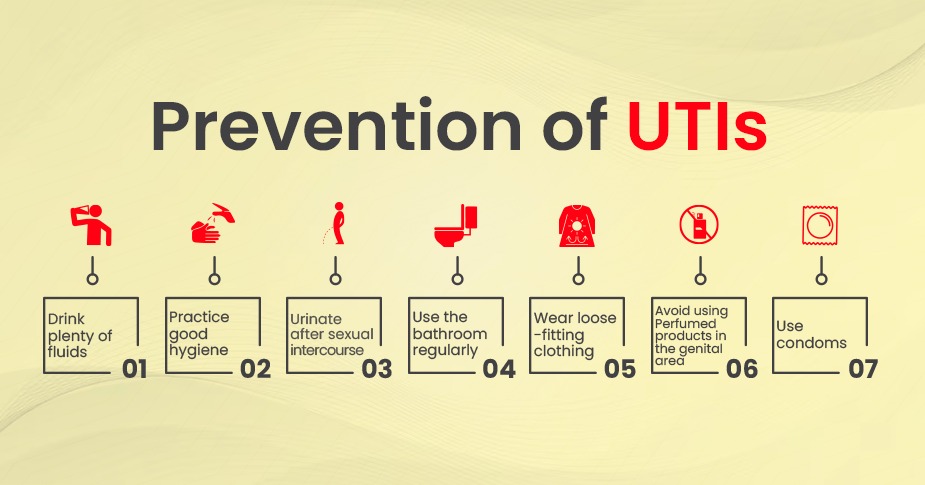
Prevention of UTIs
- Drink plenty of fluids: Water, in particular, can help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Practice good hygiene: Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom and washing your hands after urinating can help prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Urinate after sexual intercourse: Urinating after sexual intercourse can help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Use the bathroom regularly: Urinating on a regular basis can help prevent bacteria from building up in the urinary tract.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight clothing can cause irritation and increase the risk of UTIs.
- Avoid using Perfumed products in the genital area: These products can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of UTIs.
- Use condoms: Condoms can help reduce the risk of UTIs in women who are sexually active.
It is also important to seek medical treatment for a UTI as soon as possible to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys, which can cause more serious complications. If you are prone to UTIs, your healthcare provider may recommend taking preventive measures, such as taking antibiotics prophylactically or drinking cranberry juice.
Complications of UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common type of infection that can affect different parts of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, and kidneys. UTIs can range in severity from mild to severe and can have a number of complications if left untreated. Some possible complications of UTIs include:
- Kidney infection: UTIs can spread to the kidneys, leading to a more serious condition called pyelonephritis. This type of kidney infection can cause fever, back pain, and nausea.
- Sepsis: UTIs can sometimes lead to sepsis, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition in which bacteria from the infection enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
- Recurrent UTIs: UTIs that are not treated effectively or that recur frequently can lead to ongoing discomfort and disruption of daily activities.
- Complications in pregnancy: UTIs during pregnancy can cause premature labor and delivery.
- Bladder damage: UTIs can sometimes cause inflammation and damage to the bladder, leading to complications such as bladder scarring or incontinence.
With the help of this blog, we hope you now have a better understanding of UTI and its symptoms, causes, treatments, as well as its precautions. If you notice any symptoms, keep an eye on them, take precautions, and also go to a family physician for medical checkups
We hope that this article was helpful for you in understanding urinary tract infections. If you have any queries or reviews about the blog, feel free to comment below.
FAQs
Here are some commonly asked questions about UTIs:
1. How do I know if I have a UTI?
The most common symptoms of a UTI are frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and lower abdominal pain.
2. How are UTIs treated?
UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics, which can be taken orally or intravenously. There are also home remedies like drinking cranberry juice and other cranberry products.
3. What home remedies are safe to use for UTIs?
Cranberry and ursolia as a natural method effective for UTI if you have a persistent UTI.
Cranberries are rich in antioxidant compounds and contain plant compounds that reduce the urgency, frequency, and burning sensation of urination during UTI. It helps prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder and urinary tract walls.
Ursolia The main therapeutic focus of ursolia as an ingredient is that it helps to fight inflammation that comes with having a UTI, for more information please check out the link below.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/ursolic-acid

4. Can UTIs be prevented?
A healthcare provider may recommend taking preventive measures, such as taking antibiotics prophylactically or drinking cranberry juice, drinking lots of water and using hygienic practices.
5. Can UTIs cause serious complications?
If left untreated, a UTI can spread to the kidneys such as kidney damage or kidney failure.
6. What circumstances can lead to urinary tract infections?
- Constipation
- Drinking small amounts of liquid
- very concentrated urine is produced
- Residual urine after urination
- This can be detected by performing an ultrasound after urination
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8992741/#cit0001






