What is H-Pylori? Its Causes, Symptoms & its Treatment.
H.pylori is a popular & common type of gram-negative bacteria that causes H.pylori infection. H. Pylori bacteria destroys our stomach lining, a mucus layer that provides protection to our stomach against acid. This spiral-shaped bacteria stick to our stomach lining and penetrates inside the stomach where it harms the mucus, making our stomach cells injured.
H. pylori bacteria are primarily responsible for stomach and small intestine ulcers. H. pylori halts the immune response of our body which leads to various gastrointestinal disorders.
Who is affected by H.pylori? OR Who is at risk of getting H. pylori?
It may come as a surprise, H.pylori infection affects 50% of the world’s population. It’s not necessary that all individuals suffering from H.pylori infection have definite symptoms. Interestingly, only 20% of those infected have symptoms that include stomach pain, vomiting, and weight loss among others.
The thought of microorganisms invading your stomach without even having you suspect their presence in your body is indeed scary.
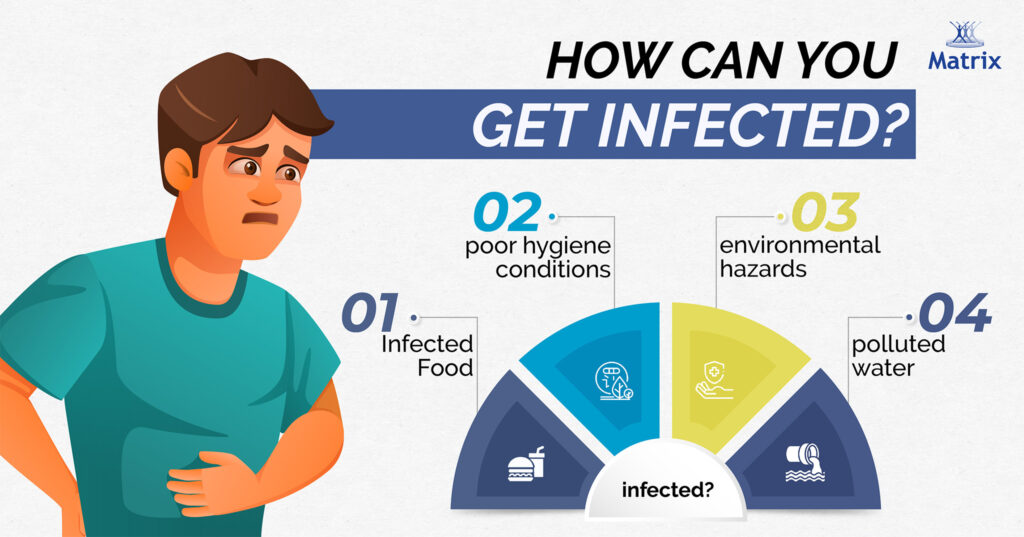
How can you get infected?
The mode of transmission of H.pylori bacteria is unclear. According to research, the bacteria are usually spread by consuming contaminated food or water. H.pylori infection is more commonly popular in developing countries because of infected food, polluted water, environmental hazards and poor hygiene conditions.
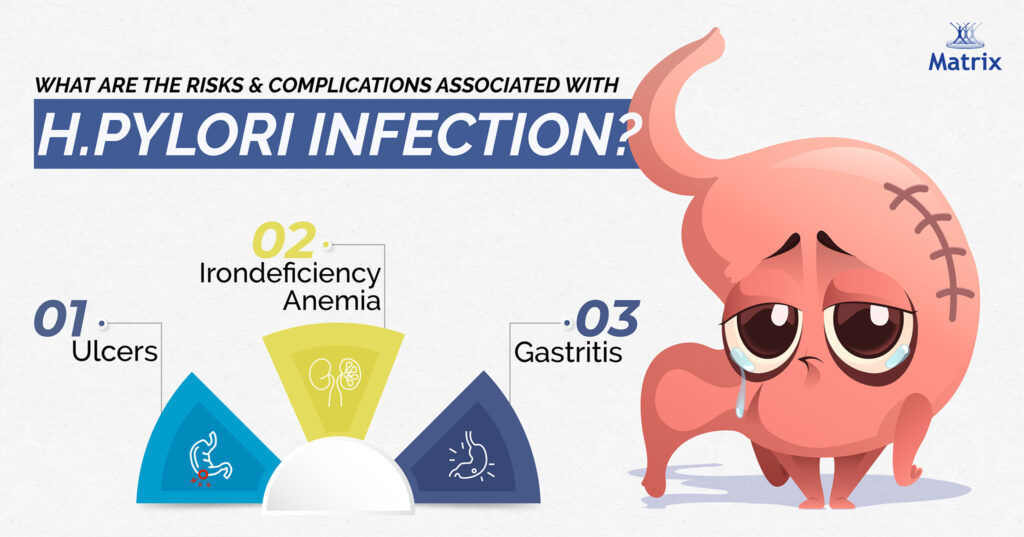
What are the risks and complications associated with H.pylori infection?
- Ulcers: H. pylori is a common cause of gastrointestinal ulcers or open sores. Acids induce corrosion of the tissue lining, leading to ulcers when the mucus layer that shields our stomach and intestines is compromised.
- Gastritis: H.pylori causes inflammation of the stomach lining leading to acute or chronic gastritis.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Chronic gastritis sometimes leads to reduced iron absorption which ultimately contributes to the development of Iron deficiency anemia.
Symptoms of an H.pylori Infection Are:
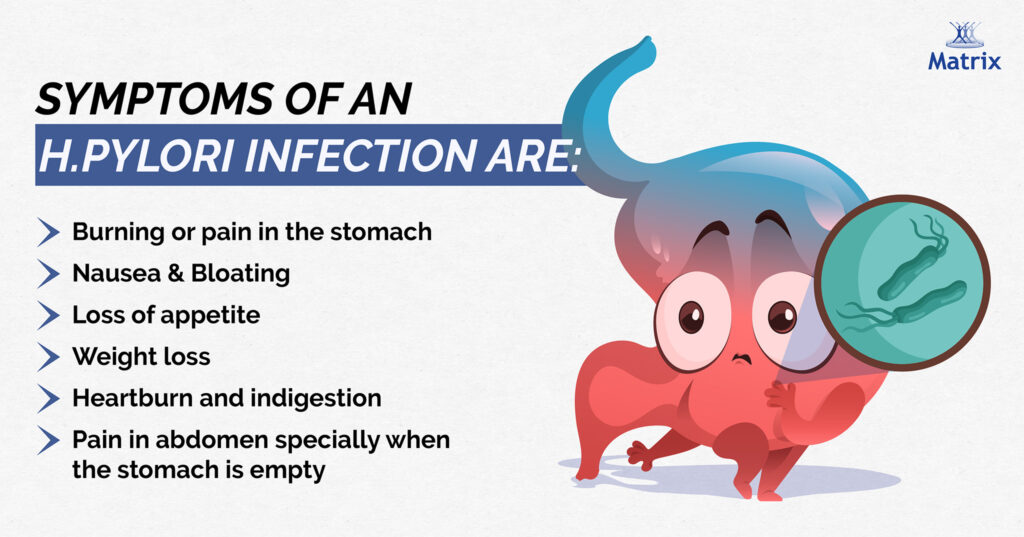
Majority of the people have no signs and symptoms of H.pylori infection. H.pylori bacteria can reside in our body for many years. Some of the main symptoms of an H.pylori infection are:
- Burning or pain in the stomach
- Nausea & Bloating
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Heartburn and indigestion
- Abdominal pain, particularly when the stomach is empty
It’s really important to know that the symptoms can vary person to person that’s why early diagnosis is the only way to confirm the possibility of the infection.
How the presence of H.pylori infection is evaluated?
Testing for H.pylori infection is important if you are experiencing any of the above-stated symptoms.
Diagnosis methods include:
- Urea Breath Test
- Stool tests
- Blood tests
- Endoscopy
How to cure H.pylori infection?
Your doctor can suggest a combination of antibiotics and other medications to treat your stomach problems, such as proton pump inhibitors, bismuth subsalicylate, etc.
Some experts suggest use of probiotics as a supplement to increase the eradication of H.pylori and reduce the side effects associated with the treatment.
ENTPRO® (Probiotic Supplement that delivers effective relief for H.pylori infection and reduce the side effect associated with the treatment)
Entpro®, a unique supplement contains a well-researched probiotic strain ‘Pylopass’ (Lactobacillus reuteri) that gets attached to the surface of H. Pylori bacteria. This prevents the bacteria from affecting the stomach lining letting Entpro® deliver total protection against H. Pylori & reducing infection in the body. Entpro® is also clinically proven to reduce inflammation and pain associated with infection.
For more information, Please contact us or visit our website; www.matrixpharma.com
References:
- Wolfgang Fischbach, Prof. Dr. med.1,* and Peter Malfertheiner, Prof. Dr. med.2. Helicobacter Pylori Infection; When to Eradicate, How to Diagnose and Treat. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Jun; 115(25): 429–436. [PubMed]
- Robert P H Logan, Marjorie M Walker. Epidemiology and diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. BMJ 2001;323:920. [PubMed]
- Mestre A, Sathiya Narayanan R, Rivas D, et al. Role of Probiotics in the Management of Helicobacter pylori. Cureus (June 30, 2022) [PubMed]
- Novozymes OneHealth. Pylopass. https://novozymesonehealth.com/products/pylopass/





